
Whether you’ve been injured in a car accident, a slip and fall, or simply woke up one morning in pain, the first step towards recovery will be understanding exactly what the root cause of your discomfort is. Modern technology allows for precise and extensive diagnostic imaging that has made it much easier for doctors to identify any injuries or conditions and begin creating plans for treatment.
For simple injuries, or to rule out things like a broken bone, you may undergo an X-ray. However, if more information is needed, you’ll likely be sent to a Marietta imaging center for further tests. A variety of scans can all provide different information, so it’s helpful to understand which tests you may have and when.
CT Scan
Sometimes called a CAT scan, a computerized tomography scan uses x-ray technology to provide more in-depth imaging. Rather than a single image, a series of X-rays are taken from different positions and combined using computer technology to create detailed images.
This more detailed scan gives much more visibility into the body, allowing it to be viewed from multiple angles. CT scans provide a 3D image, so while you may find similar injuries that you would with an x-ray, they are more detailed in precise. This can be especially beneficial when detecting small things like tumors, or for identifying internal bleeding.
CT scans contain radiation, so they should be used in moderation. The body can be at risk of overexposure if it undergoes an x-ray or CT scan too often. For this reason, working with an expert radiologist is important. They will understand the limits your body has and work with you to determine the right scans for your needs.
Applications
- Injury Detection: CT scans are excellent for detecting fractures, internal bleeding, and injuries to soft tissues and organs.
- Cancer Screening: Used to locate tumors, determine their size, and monitor progress.
- Vascular Conditions: CT scans can also visualize blood vessels and detect conditions like aneurysms and blockages.
Advantages
- Speed: CT scans are quick, often completed in a few minutes.
- Detail: Provide detailed images of bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues.
MRI
 Magnetic resonance imaging, or an MRI, is a type of scan that does not rely on radiation, but instead uses a combination of radio waves and magnetic force to produce images. These images are different than what you would see in an x-ray or CT scan, though they may help identify similar disorders.
Magnetic resonance imaging, or an MRI, is a type of scan that does not rely on radiation, but instead uses a combination of radio waves and magnetic force to produce images. These images are different than what you would see in an x-ray or CT scan, though they may help identify similar disorders.
MRIs are most often used to identify any damaged tissues in the body, like a torn ligament, though they can also identify problems like a broken bone. Often when a CT scan or x-ray doesn’t provide enough detail, an MRI will be ordered to get more information.
You might be wondering what to expect when getting an MRI. The process of getting an MRI can be daunting for some people. In most cases, you will be placed inside a large metal tube that produces the images while you lie still. This can take upwards of 90 minutes, depending on the type and number of images needed. You may be given a contrast dye to ingest to help make images clearer. Nothing about an MRI is painful, but the enclosed space of the tube induces anxiety for some people. You can ask your Marietta imaging center if they offer open MRIs or sedatives if you are worried about severe claustrophobia.
Applications
- Neurological Imaging: MRIs are especially effective for brain and spinal cord imaging.
- Soft Tissue Imaging: Excellent for detecting abnormalities in soft tissues, such as tumors or infections.
Advantages
- No Radiation: MRIs do not use radiation, making them safer for repeated use.
- Detailed Soft Tissue Images: Provide superior images of soft tissues compared to CT scans.
PET Scan
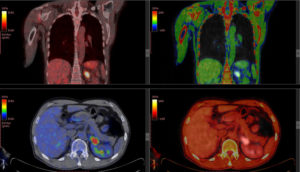
Positron emission tomography, or PET scan, is a kind of imaging that uses small particles entered into the bloodstream in order to view bodily organs by using the flow of blood as a delivery mechanism. Before a PET scan, a radiologist will inject a liquid containing small amounts of radiation into your vein, allowing it to spread through the bloodstream. Blood usually collects near affected organs, meaning this liquid will do the same. A scanner can then be passed over your body to pick up radiation in the blood, and the images are transmitted to a computer for viewing.
A PET scan is most often used for organ and blood-related disorders, as well as documenting certain brain activity. They can also be used to test various forms of treatment for cancer and other illnesses. One of the main differences between MRI and PET scans is that a PET scan produces less detailed images. Because of this, you may see your radiologist use a PET-CT scan, which combines the images of both tools to create a more accurate picture. This is especially common when scans are being used to identify cancers.
Applications
- Cancer Detection and Monitoring: PET scans are highly effective in identifying cancerous cells and monitoring the effectiveness of cancer treatment.
- Neurological Disorders: They help in diagnosing neurological conditions like epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.
- Cardiology: PET scans assess blood flow to the heart and identify areas of reduced blood flow.
Advantages
- Functional Imaging: PET scans provide information about the metabolic activity of tissues and organs, which is crucial for detecting diseases early.
- Combination Scans: Can be combined with CT scans (PET-CT) to provide more detailed information.
Comparing PET Scan vs. MRI vs. CT Scan
Understanding the difference between PET scan and CT scan and MRI is essential for both patients and healthcare providers alike. Comparing these types of diagnostic imaging tools highlights their distinct advantages and considerations associated with PET scan versus MRI versus CT scan, empowering you to make informed decisions about your healthcare journey.
Radiation Exposure
One of the primary differences among PET scans, CT scans, and MRIs is the level of radiation exposure.
- PET Scans and CT Scans: Both PET and CT scans use ionizing radiation. In PET scans, a small amount of radioactive material called a tracer is injected into your body, which interacts with electrons in your body. CT scans, on the other hand, use X-rays to create detailed images. The radiation dose from a single CT scan is generally higher than that from a typical X-ray but still within safe limits for diagnostic purposes. Repeated exposure to radiation, however, can increase the risk of developing cancer over a person’s lifetime.
- MRI: MRI does not involve radiation. Instead, it uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to generate images. This makes MRI a safer option for patients who need multiple scans over time or for those who are particularly sensitive to radiation, such as pregnant women and young children.
Imaging Detail
The level of detail and the type of tissues best visualized also vary among these diagnostic imaging techniques.
- MRI: MRIs are superior for imaging soft tissues. They provide high-resolution images of organs, muscles, tendons, and the brain. This makes MRIs particularly useful for diagnosing conditions related to the brain and spinal cord, joints, and soft tissue structures.
- CT Scan: CT scans are excellent for imaging bones, detecting fractures, and looking at blood vessels. They provide detailed cross-sectional images that are very useful for diagnosing internal injuries, detecting tumors, and planning surgeries.
- PET Scan: PET scans are excellent for showing how well different parts of the body are working, and they are known as functional imaging. They provide information about the metabolic activity of tissues, which is crucial for detecting cancers, assessing brain function, and monitoring the effects of various treatments. In certain situations, PET scans can identify abnormalities even before structural changes show up on CT or MRI.
Speed and Convenience
The time required to perform these types of diagnostic scans and the convenience for you as the patient can also be important factors.
- CT Scan: CT scans are the fastest imaging option among the three. A typical CT scan can be completed in just a few minutes. This makes CT scans very convenient for emergency situations where time is critical, such as trauma or stroke.
- MRI: MRI scans typically take longer than CT scans. A full MRI scan can take anywhere from 15 minutes to over an hour, depending on the area being examined and the level of detail required. The patient must remain still during the scan, which can be challenging for some people. Additionally, the MRI machine can be noisy and confined, which might be uncomfortable for patients with claustrophobia.
- PET Scan: PET scans also take longer than CT scans but generally less time than MRIs. The entire procedure, including the time needed for the radiotracer to circulate in the body, can take up to a few hours. However, the actual imaging process for a PET scan is relatively quick.
Choosing the Appropriate Imaging Tool
Selecting the appropriate imaging technique depends on the specific medical condition and the diagnostic information needed.
- PET Scans: These are invaluable for functional imaging, particularly in cancer detection and monitoring, as they can reveal metabolic changes in tissues. PET scans are also beneficial for diagnosing neurological disorders and evaluating heart disease.
- CT Scans: CT scans provide quick and detailed images of bones, organs, and blood vessels. They are often used in emergency settings to diagnose internal injuries, detect tumors, and guide surgical planning.
- MRIs: MRIs offer unparalleled detail for soft tissue evaluation and are the preferred choice for imaging the brain, spinal cord, joints, and soft tissues. They are especially useful for diagnosing neurological conditions, musculoskeletal disorders, and detecting soft tissue abnormalities.
The Right Scan for You at AICA Marietta
If you need to undergo diagnostic imaging, you’ll want to work with an expert to determine what scan is best for you. This decision will be a combination of factors, including the risk associated with radiation levels and what you may be looking to diagnose. At AICA Marietta, our Marietta imaging center is filled with specialists who are here to help you understand any tests and the results of those tests. Then, they will work to create personalized plans for recovery based on this information. One of the things they could suggest is chiropractic treatment for your injuries and pain. Contact AICA Marietta today to schedule your first appointment!